Gene editing for collagen disorders: current advances and future perspectives
Liu D, Nikoo M, Boran G, Zhou P, Regenstein J Collagen and gelatin. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2015;6:527–57.
Tarnutzer K, Siva Sankar D, Dengjel J, Ewald CY. Collagen constitutes about 12% in females and 17% in males of the total protein in mice. Sci Rep. 2023;13:4490.
Google Scholar
Fidler AL, Boudko SP, Rokas A, Hudson BG. The triple helix of collagens – an ancient protein structure that enabled animal multicellularity and tissue evolution. J Cell Sci. 2018;131:jcs203950.
Google Scholar
Gjaltema RAF, Bank RA. Molecular insights into prolyl and lysyl hydroxylation of fibrillar collagens in health and disease. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;52:74–95.
Google Scholar
Fujii KK, Taga Y, Takagi YK, Masuda R, Hattori S, Koide T The thermal stability of the collagen triple helix is tuned according to the environmental temperature. Int J Mol Sci [Internet]. 2022; 23:2040.
Myllyharju J, Kivirikko KI. Collagens, modifying enzymes and their mutations in humans, flies and worms. Trends Genet. 2004;20:33–43.
Google Scholar
Cao L, Zhang Z, Yuan D, Yu M, Min J Tissue engineering applications of recombinant human collagen: a review of recent progress. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:135846.
Ricard-Blum S The Collagen Family. 2011;3:a004978.
Shoulders MD, Raines RT. Collagen structure and stability. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:929–58.
Google Scholar
Gatseva A, Sin YY, Brezzo G, Van Agtmael T. Basement membrane collagens and disease mechanisms. Essays Biochem. 2019;63:297–312.
Google Scholar
Zeltz C, Gullberg D. The integrin–collagen connection – a glue for tissue repair? J Cell Sci. 2016;129:653–64.
Google Scholar
Juskaite V, Corcoran DS, Leitinger B. Collagen induces activation of DDR1 through lateral dimer association and phosphorylation between dimers. eLife. 2017;6:e25716.
Google Scholar
Park K, Jayadev R, Payne SG, Kenny-Ganzert IW, Chi Q, Costa DS, et al. Reciprocal discoidin domain receptor signaling strengthens integrin adhesion to connect adjacent tissues. eLife. 2023;12:RP87037.
Google Scholar
Borza CM, Bolas G, Zhang X, Browning Monroe MB, Zhang M-Z, Meiler J, et al. The collagen receptor discoidin domain receptor 1b enhances integrin β1-mediated cell migration by interacting with talin and promoting Rac1 activation. Front Cell Develop Biol. 2022;10. 836797.
Google Scholar
Jariwala N, Ozols M, Bell M, Bradley E, Gilmore A, Debelle L, et al. Matrikines as mediators of tissue remodelling. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;185:114240.
Google Scholar
Mavrogonatou E, Papadopoulou A, Pratsinis H, Kletsas D. Senescence-associated alterations in the extracellular matrix: deciphering their role in the regulation of cellular function. Am J. 2023;325:C633–C47.
Google Scholar
Winkler J, Abisoye-Ogunniyan A, Metcalf KJ, Werb Z. Concepts of extracellular matrix remodelling in tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Commun. 2020;11:5120.
Google Scholar
Pickup MW, Mouw JK, Weaver VM. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014;15:1243–53.
Google Scholar
Stylianopoulos T, Munn LL, Jain RK. Reengineering the physical microenvironment of tumors to improve drug delivery and efficacy: from mathematical modeling to bench to bedside. Trends Cancer. 2018;4:292–319.
Google Scholar
Jeanne M, Gould DB. Genotype-phenotype correlations in pathology caused by collagen type IV alpha 1 and 2 mutations. Matrix Biol. 2017;57-58:29–44.
Google Scholar
Butterfield RJ, Foley AR, Dastgir J, Asman S, Dunn DM, Zou Y, et al. Position of glycine substitutions in the triple helix of 61, 62, and 63 is correlated with severity and mode of inheritance in collagen VI myopathies. Hum Mutat. 2013;34:1558–67.
Google Scholar
Sałacińska K, Pinkier I, Rutkowska L, Chlebna-Sokół D, Jakubowska-Pietkiewicz E, Michałus I, et al. Novel mutations within collagen Alpha1(I) and Alpha2(I) ligand-binding sites, broadening the spectrum of osteogenesis imperfecta – current insights into collagen Type I Lethal Regions. Front Genet. 2021;12:692978.
Omar R, Lee MAW, Gonzalez-Trueba L, Thomson CR, Hansen U, Lianos S, et al. The chemical chaperone 4-phenylbutyric acid rescues molecular cell defects of COL3A1 mutations that cause vascular Ehlers Danlos syndrome. Cell Death Discov. 2025;11:200.
Google Scholar
Mullan LA, Mularczyk EJ, Kung LH, Forouhan M, Wragg JMA, Goodacre R, et al. Increased intracellular proteolysis reduces disease severity in an ER stress–associated dwarfism. J Clin Investig. 2017;127:3861–5.
Google Scholar
Lamandé SR Collagen VI Muscle disorders: mutation types, pathogenic mechanisms and approaches to therapy. In: Halper J, editor. Progress in Heritable Soft Connective Tissue Diseases. Springer International Publishing; 2021. p. 311–23.
Guide SV, Gonzalez ME, Bagci IS, Agostini B, Chen H, Feeney G, et al. Trial of beremagene geperpavec (B-VEC) for dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:2211–9.
Google Scholar
Mali P, Yang L, Esvelt KM, Aach J, Guell M, DiCarlo JE, et al. RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science. 2013;339:823–6.
Google Scholar
Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, Hauer M, Doudna JA, Charpentier E. A programmable dual-RNA–guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science. 2012;337:816–21.
Google Scholar
Liu M, Zhang W, Xin C, Yin J, Shang Y, Ai C, et al. Global detection of DNA repair outcomes induced by CRISPR–Cas9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:8732–42.
Google Scholar
Komor AC, Kim YB, Packer MS, Zuris JA, Liu DR. Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage. Nature. 2016;533:420–4.
Google Scholar
Anzalone AV, Randolph PB, Davis JR, Sousa AA, Koblan LW, Levy JM, et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature. 2019;576:149–57.
Google Scholar
Porto EM, Komor AC, Slaymaker IM, Yeo GW. Base editing: advances and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19:839–59.
Google Scholar
Woodley DT, Keene DR, Atha T, Huang Y, Ram R, Kasahara N, et al. Intradermal injection of lentiviral vectors corrects regenerated human dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa skin tissue in vivo. Mol Ther. 2004;10:318–26.
Google Scholar
Lwin SM, Syed F, Di WL, Kadiyirire T, Liu L, Guy A, et al. Safety and early efficacy outcomes for lentiviral fibroblast gene therapy in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. JCI Insight. 2019;4:e126243.
Lim J, Grafe I, Alexander S, Lee B. Genetic causes and mechanisms of osteogenesis imperfecta. Bone. 2017;102:40–9.
Google Scholar
Jung H, Rim YA, Park N, Nam Y, Ju JH. Restoration of osteogenesis by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing of the mutated COL1A1 gene in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Clin Med. 2021;10:3141.
Google Scholar
Fus-Kujawa A, Mendrek B, Bajdak-Rusinek K, Diak N, Strzelec K, Gutmajster E, et al. Gene-repaired iPS cells as novel approach for patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1205122.
Google Scholar
Cao Y, Li L, Ren X, Mao B, Yang Y, Mi H, et al. CRISPR/Cas9 correction of a dominant cis-double-variant in COL1A1 isolated from a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta increases the osteogenic capacity of induced pluripotent stem cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38:719–32.
Google Scholar
Yang Y-S, Sato T, Chaugule S, Ma H, Xie J, Gao G, et al. AAV-based gene editing of type 1 collagen mutation to treat osteogenesis imperfecta. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024;35:102111.
Malfait F, Castori M, Francomano CA, Giunta C, Kosho T, Byers PH. The Ehlers–Danlos syndromes. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2020;6:64.
Google Scholar
Gensure RC, Mäkitie O, Barclay C, Chan C, DePalma SR, Bastepe M, et al. A novel COL1A1 mutation in infantile cortical hyperostosis (Caffey disease) expands the spectrum of collagen-related disorders. J Clin Investig. 2005;115:1250–7.
Google Scholar
Alamowitch S, Plaisier E, Favrole P, Prost C, Chen Z, Van Agtmael T, et al. Cerebrovascular disease related to COL4A1 mutations in HANAC syndrome. Neurology. 2009;73:1873–82.
Google Scholar
Warady BA, Agarwal R, Bangalore S, Chapman A, Levin A, Stenvinkel P, et al. Alport syndrome classification and management. Kidney Med. 2020;2:639–49.
Google Scholar
Xie J, Wu X, Ren H, Wang W, Wang Z, Pan X, et al. COL4A3 mutations cause focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. J Mol Cell Biol. 2014;6:498–505.
Google Scholar
Wang YY, Rana K, Tonna S, Lin T, Sin L, Savige J. COL4A3 mutations and their clinical consequences in thin basement membrane nephropathy (TBMN)1. Kidney Int. 2004;65:786–90.
Google Scholar
Daga S, Donati F, Capitani K, Croci S, Tita R, Giliberti A, et al. New frontiers to cure Alport syndrome: COL4A3 and COL4A5 gene editing in podocyte-lineage cells. Eur J Hum Genet. 2020;28:480–90.
Google Scholar
Kashtan CE, Ding J, Garosi G, Heidet L, Massella L, Nakanishi K, et al. Alport syndrome: a unified classification of genetic disorders of collagen IV alpha345: a position paper of the Alport Syndrome Classification Working Group. Kidney Int. 2018;93:1045–51.
Google Scholar
Lampe AK, Dunn DM, von Niederhausern AC, Hamil C, Aoyagi A, Laval SH, et al. Automated genomic sequence analysis of the three collagen VI genes: applications to Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy and Bethlem myopathy. J Med Genet. 2005;42:108.
Google Scholar
Benati D, Cattin E, Corradi F, Ferrari T, Pedrazzoli E, Patrizi C, et al. Restored collagen VI microfilaments network in the extracellular matrix of CRISPR-edited Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy fibroblasts. Biomolecules. 2024;14:1412.
López-Márquez A, Morín M, Fernández-Peñalver S, Badosa C, Hernández-Delgado A, Natera-de Benito D, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated allele-specific disruption of a dominant COL6A1 pathogenic variant improves collagen VI network in patient fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci [Internet]. 2022; 23:4410.
Bolduc V, Zou Y, Ko D, Bönnemann CG. siRNA-mediated Allele-specific silencing of a COL6A3 mutation in a cellular model of dominant ullrich muscular dystrophy. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2014;3:e147.
Google Scholar
Marrosu E, Ala P, Muntoni F, Zhou H. Gapmer antisense oligonucleotides suppress the mutant Allele of COL6A3 and restore functional protein in ullrich muscular dystrophy. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;8:416–27.
Google Scholar
Watanabe M, Natsuga K, Shinkuma S, Shimizu H. Epidermal aspects of type VII collagen: Implications for dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. J Dermatol. 2018;45:515–21.
Google Scholar
Nyström A, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Kiritsi D Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: secondary disease mechanisms and disease modifiers. Front Genet. 2021;12:737272.
Siprashvili Z, Nguyen NT, Gorell ES, Loutit K, Khuu P, Furukawa LK, et al. Safety and wound outcomes following genetically corrected autologous epidermal grafts in patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. JAMA. 2016;316:1808–17.
Google Scholar
So JY, Nazaroff J, Iwummadu CV, Harris N, Gorell ES, Fulchand S, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of gene-corrected autologous keratinocyte grafts for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022;17:377.
Google Scholar
Bonafont J, Mencía A, Chacón-Solano E, Srifa W, Vaidyanathan S, Romano R, et al. Correction of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa by homology-directed repair-mediated genome editing. Mol Ther. 2021;29:2008–18.
Google Scholar
Izmiryan A, Ganier C, Bovolenta M, Schmitt A, Mavilio F, Hovnanian A. Ex Vivo COL7A1 correction for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa using CRISPR/Cas9 and homology-directed repair. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;12:554–67.
Google Scholar
Hong SA, Kim SE, Lee AY, Hwang GH, Kim JH, Iwata H, et al. Therapeutic base editing and prime editing of COL7A1 mutations in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Mol Ther. 2022;30:2664–79.
Google Scholar
Naso G, Gkazi SA, Georgiadis C, Jayarajan V, Jacków J, Fleck R, et al. Cytosine deaminase base editing to restore COL7A1 in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa human: murine skin model. JID Innov. 2023;3:100191.
Google Scholar
Sheriff A, Guri I, Zebrowska P, Llopis-Hernandez V, Brooks IR, Tekkela S, et al. ABE8e adenine base editor precisely and efficiently corrects a recurrent COL7A1 nonsense mutation. Sci Rep. 2022;12:19643.
Google Scholar
Mustfa SA, Dimitrievska M, Wang C, Gu C, Sun N, Romańczuk K, et al. Porous silicon nanoneedles efficiently deliver adenine base editor to correct a recurrent pathogenic COL7A1 variant in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Adv Mater. 2025;37:2414728.
Petković I, Bischof J, Kocher T, March OP, Liemberger B, Hainzl S, et al. COL17A1 editing via homology-directed repair in junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Frontiers in Medicine. 2022;9:976604.
Carusillo A, Haider S, Schäfer R, Rhiel M, Türk D, Chmielewski Kay O, et al. A novel Cas9 fusion protein promotes targeted genome editing with reduced mutational burden in primary human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51:4660–73.
Google Scholar
Nambiar TS, Billon P, Diedenhofen G, Hayward SB, Taglialatela A, Cai K, et al. Stimulation of CRISPR-mediated homology-directed repair by an engineered RAD18 variant. Nat Commun. 2019;10:3395.
Google Scholar
Antoniou P, Miccio A, Brusson M Base and prime editing technologies for blood disorders. Front Genome Edit. 2021;3:618406.
Davis JR, Wang X, Witte IP, Huang TP, Levy JM, Raguram A, et al. Efficient in vivo base editing via single adeno-associated viruses with size-optimized genomes encoding compact adenine base editors. Nat Biomed Eng. 2022;6:1272–83.
Google Scholar
Hu Z, Wang Y, Liu Q, Qiu Y, Zhong Z, Li K, et al. Improving the precision of base editing by bubble hairpin single guide RNA. mBio. 2021;12:e00342.
Cócera-Ortega L and Wilders R and Kamps SC, Fabrizi B, Huber I, van der Made I et al. shRNAs targeting a common KCNQ1 variant could alleviate long-QT1 disease severity by inhibiting a mutant allele. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:4053.
Wang D, Tai PWL, Gao G. Adeno-associated virus vector as a platform for gene therapy delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019;18:358–78.
Google Scholar
Hunt JMT, Samson CA, Rand AD, Sheppard HM. Unintended CRISPR-Cas9 editing outcomes: a review of the detection and prevalence of structural variants generated by gene-editing in human cells. Hum Genet. 2023;142:705–20.
Google Scholar
Issa SS, Shaimardanova AA, Solovyeva VV, Rizvanov AA Various AAV Serotypes and their applications in gene therapy: an overview. Cells [Internet]. 2023; 12:785.
Barbon E, Kawecki C, Marmier S, Sakkal A, Collaud F, Charles S, et al. Development of a dual hybrid AAV vector for endothelial-targeted expression of von Willebrand factor. Gene Ther. 2023;30:245–54.
Google Scholar
Fredman G, Kamaly N, Spolitu S, Milton J, Ghorpade D, Chiasson R, et al. Targeted nanoparticles containing the proresolving peptide Ac2-26 protect against advanced atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic mice. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7:275ra20–ra20.
Google Scholar
Zhang S, Shen J, Li D, Cheng Y. Strategies in the delivery of Cas9 ribonucleoprotein for CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. Theranostics. 2021;11:614–48.
Google Scholar
Berthault C, Gaucher S, Gouin O, Schmitt A, Chen M, Woodley D, et al. J Investig Dermatol. 2024;144:1322–33.
Google Scholar
Wang X, Wang X, Li Y, A S, Qiu B, Bushmalyova A, et al. CRISPR-Cas9-based non-viral gene editing therapy for topical treatment of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Mol Ther Methods Clin Develop. 2023;31:101304.
Lindley SR, Subbaiah KCV, Priyanka F, Poosala P, Ma Y, Jalinous L, et al. Ribozyme-activated mRNA trans-ligation enables large gene delivery to treat muscular dystrophies. Science. 2024;386:762–7.
Google Scholar
Yarnall MTN, Ioannidi EI, Schmitt-Ulms C, Krajeski RN, Lim J, Villiger L, et al. Drag-and-drop genome insertion of large sequences without double-strand DNA cleavage using CRISPR-directed integrases. Nat Biotechnol. 2023;41:500–12.
Google Scholar
Bax BD, Sutormin D, McDonald NQ, Burley GA, Shelkovnikova T Oligonucleotide-Recognizing topoisomerase inhibitors (OTIs): precision gene editors for neurodegenerative diseases? Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:11541.
Woolf TM, Chase JM, Stinchcomb DT. Toward the therapeutic editing of mutated RNA sequences. PNAS. 1995;92:8298–302.
Google Scholar
Fukuda M, Umeno H, Nose K, Nishitarumizu A, Noguchi R, Nakagawa H. Construction of a guide-RNA for site-directed RNA mutagenesis utilising intracellular A-to-I RNA editing. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41478.
Google Scholar
Montiel-Gonzalez MF, Vallecillo-Viejo I, Yudowski GA, Rosenthal JJC. Correction of mutations within the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator by site-directed RNA editing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:18285–90.
Google Scholar
Pfeiffer LS, Stafforst T. Precision RNA base editing with engineered and endogenous effectors. Nat Biotechnol. 2023;41:1526–42.
Google Scholar
Merkle T, Merz S, Reautschnig P, Blaha A, Li Q, Vogel P, et al. Precise RNA editing by recruiting endogenous ADARs with antisense oligonucleotides. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37:133–8.
Google Scholar
Qu L, Yi Z, Zhu S, Wang C, Cao Z, Zhou Z, et al. Programmable RNA editing by recruiting endogenous ADAR using engineered RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37:1059–69.
Google Scholar
Reautschnig P, Fruhner C, Wahn N, Wiegand CP, Kragness S, Yung JF, et al. Precise in vivo RNA base editing with a wobble-enhanced circular CLUSTER guide RNA. Nat Biotechnol. 2024;43:545–57.
Manfredsson FP, Rising AC, Mandel RJ. AAV9: a potential blood-brain barrier buster. Mol Ther. 2009;17:403–5.
Google Scholar
Riedmayr LM, Hinrichsmeyer KS, Thalhammer SB, Mittas DM, Karguth N, Otify DY, et al. mRNA trans-splicing dual AAV vectors for (epi)genome editing and gene therapy. Nat Commun. 2023;14:6578.
Google Scholar
Infante Lara L, Fenner S, Ratcliffe S, Isidro-Llobet A, Hann M, Bax B, et al. Coupling the core of the anticancer drug etoposide to an oligonucleotide induces topoisomerase II-mediated cleavage at specific DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:2218–33.
Google Scholar
Barat-Houari M, Sarrabay G, Gatinois V, Fabre A, Dumont B, Genevieve D, et al. Mutation update for COL2A1 gene variants associated with type II collagenopathies. Hum Mutat. 2016;37:7–15.
Google Scholar
Van Camp G, Snoeckx RL, Hilgert N, van den Ende J, Fukuoka H, Wagatsuma M, et al. A new autosomal recessive form of stickler syndrome is caused by a mutation in the COL9A1 Gene. Am J Hum Genet. 2006;79:449–57.
Google Scholar
Omar R, Malfait F, Van Agtmael T. Four decades in the making: collagen III and mechanisms of vascular Ehlers Danlos syndrome. Matrix Biol. 2021;12:100090.
Google Scholar
Zhou X, Wang J, Mao J, Ye Q Clinical manifestations of alport syndrome-diffuse leiomyomatosis patients with contiguous gene deletions in COL4A6 and COL4A5. Front Med. 2021;8:766224.
Liu X, Zheng T, Zhao C, Zhang Y, Liu H, Wang L, et al. Genetic mutations and molecular mechanisms of Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Eye Vis. 2021;8:24.
Google Scholar
Lamandé SR, Bateman JF. Genetic disorders of the extracellular matrix. Anat Rec. 2020;303:1527–42.
Google Scholar
Nixon TRW, Alexander P, Richards A, McNinch A, Bearcroft PWP, Cobben J, et al. Homozygous Type IX collagen variants (COL9A1, COL9A2, and COL9A3) causing recessive Stickler syndrome—expanding the phenotype. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2019;179:1498–506.
Google Scholar
Dennis EP, Greenhalgh-Maychell PL, Briggs MD. Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia and related disorders: Molecular genetics, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic avenues. Develop Dyn. 2021;250:345–59.
Google Scholar
Czarny-Ratajczak M, Lohiniva J, Rogala P, Kozlowski K, Perälä M, Carter L, et al. A mutation in COL9A1 causes multiple epiphyseal dysplasia: further evidence for locus heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 2001;69:969–80.
Google Scholar
Al Kaissi A, Ghachem MB, Nabil NM, Kenis V, Melchenko E, Morenko E, et al. Schmid’s type of metaphyseal chondrodysplasia: diagnosis and management. Orthop Surg. 2018;10:241–6.
Google Scholar
El Sherif R, Saito Y, Hussein RS, Izu Y, Koch M, Noguchi S, et al. A novel homozygous nonsense variant in COL12A1 causes myopathic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: a case report and literature review. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2024;50:e13004.
Google Scholar
Rodríguez Cruz PM, Cossins J, de Paula Estephan E, Munell F, Selby K, Hirano M, et al. The clinical spectrum of the congenital myasthenic syndrome resulting from COL13A1 mutations. Brain. 2019;142:1547–60.
Google Scholar
Jonsson F, Byström B, Davidson AE, Backman LJ, Kellgren TG, Tuft SJ, et al. Mutations in collagen, type XVII, Alpha 1 (COL17A1) cause epithelial recurrent erosion dystrophy (ERED). Hum Mutat. 2015;36:463–73.
Google Scholar
Hull S, Arno G, Ku CA, Ge Z, Waseem N, Chandra A, et al. Molecular and clinical findings in patients with Knobloch syndrome. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016;134:753–62.
Google Scholar
Natera-de Benito D, Jurgens JA, Yeung A, Zaharieva IT, Manzur A, DiTroia SP, et al. Recessive variants in COL25A1 gene as novel cause of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita with ocular congenital cranial dysinnervation disorder. Hum Mutat. 2022;43:487–98.
Google Scholar
Evie K, Athina T, Nayia N, Angelos A, Ioannis P, Elisavet E, et al. First reported case of Steel syndrome in the European population: A novel homozygous mutation in COL27A1 and review of the literature. Eur J Med Genet. 2020;63:103939.
Google Scholar
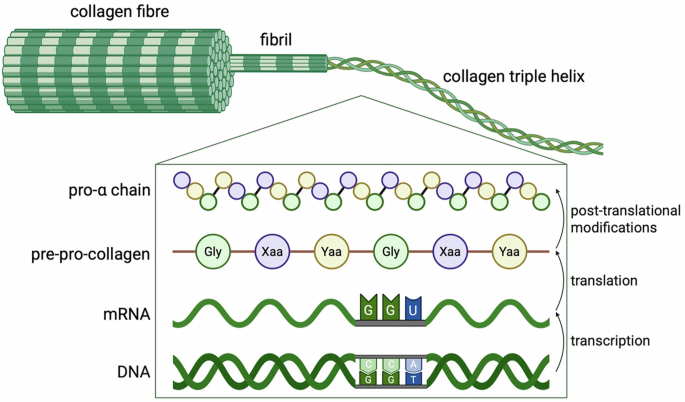
Holmes DF, Lu Y, Starborg T, Kadler KE Chapter Three – Collagen Fibril Assembly and Function. In: Litscher ES, Wassarman PM, editors. Curr Top Develop Biol. 130: Academic Press; 2018. p. 107–42.
link








